TCB: Fast Facts
Fiscal Year 2021 Overview
Trade capacity building (TCB) plays a critical part in the United States' strategy to enable developing countries to implement the market-opening reforms necessary for trade agreement compliance and foster economic growth from increased trade and investment. The United States is the largest single-country provider of trade-related assistance (also called TCB).
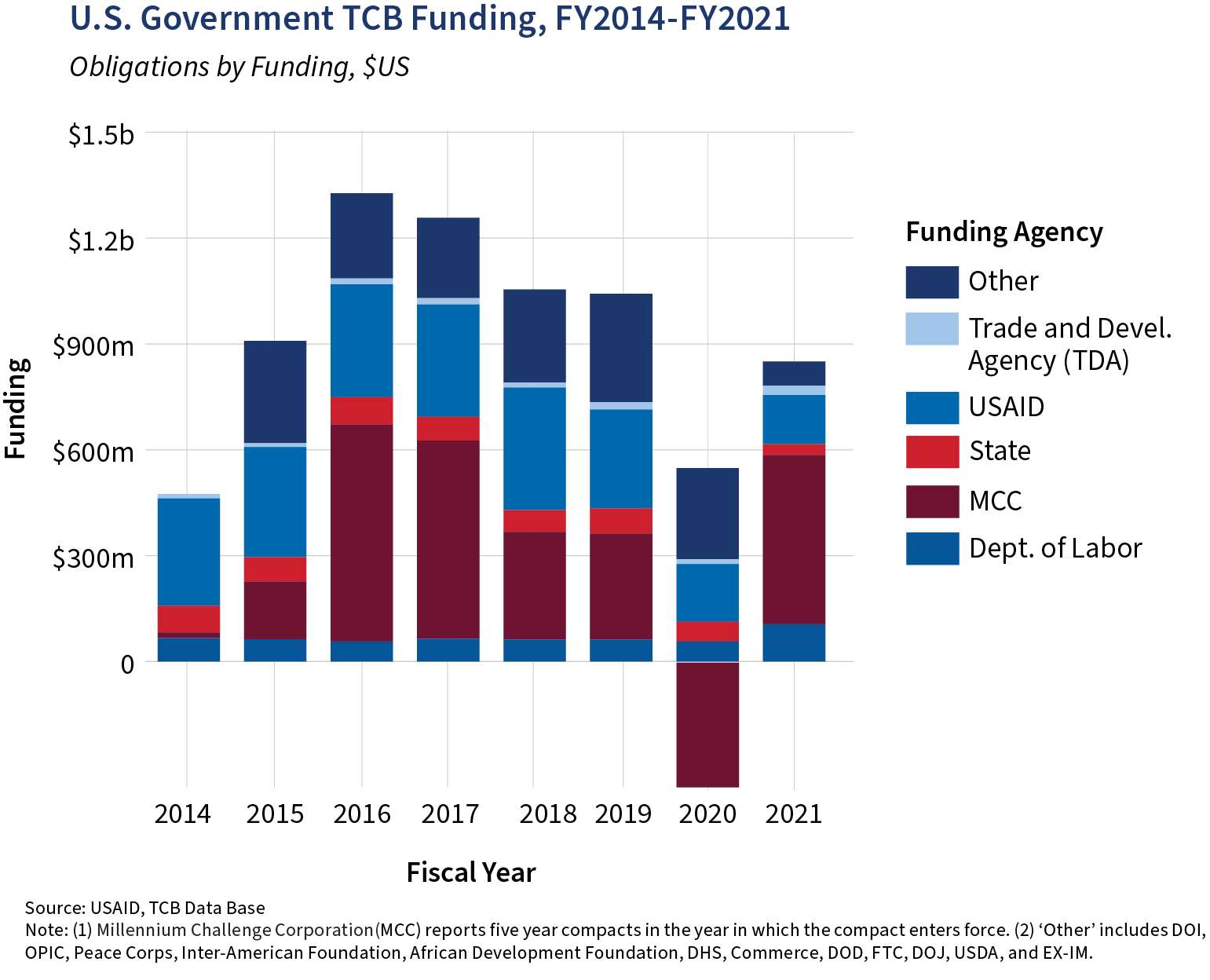
The U.S. government's trade capacity building (TCB) obligations totaled $851m in FY2021,
with investments in 511 activities
across 96 countries, geographic regions, or trade groups.
Top Three Largest Funders of TCB-Related Activities
- $479m Millennium Challenge Corporation (MCC)
- $139m U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)
- $105m Department of Labor (DOL)
Top Three Largest Funders of TCB-Related Activities
- $500m Trade-related Infrastructure
- $120m Trade-related Labor
Increases in Funding by Agency
FY2020-FY2021
354%
MCC +668m
95%
Trade and Development Agency +13m
86%
DOL +48m
Decreases in Funding by Agency
FY2020-FY2021
92%
Department of Agriculture
68%
Department of Commerce (DOC)
48%
Department of State (DOS)
Total US Obligation Increase
FY2020-FY2021
137%
The increase in total USG obligations can be primarily attributed to the obligations made under MCC's Senegal Compact.

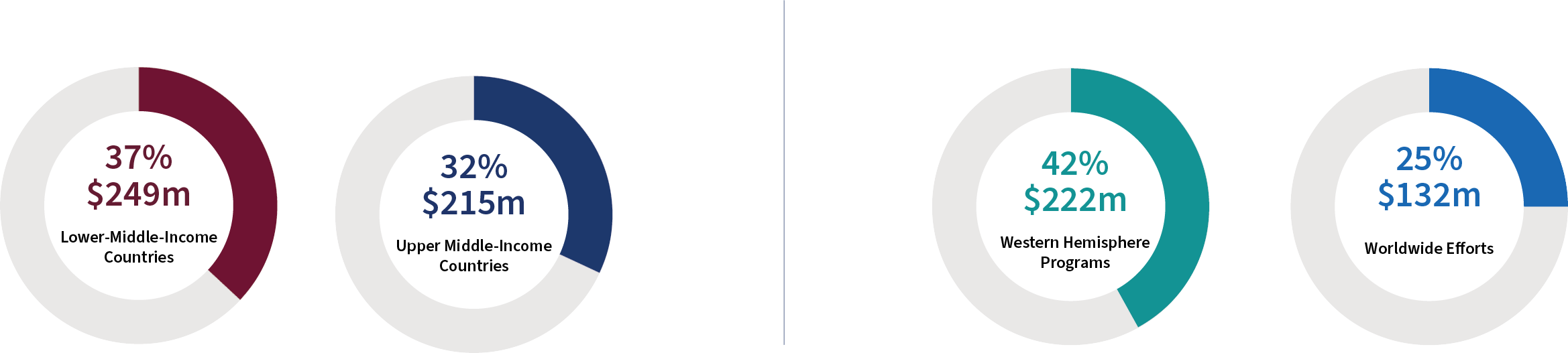
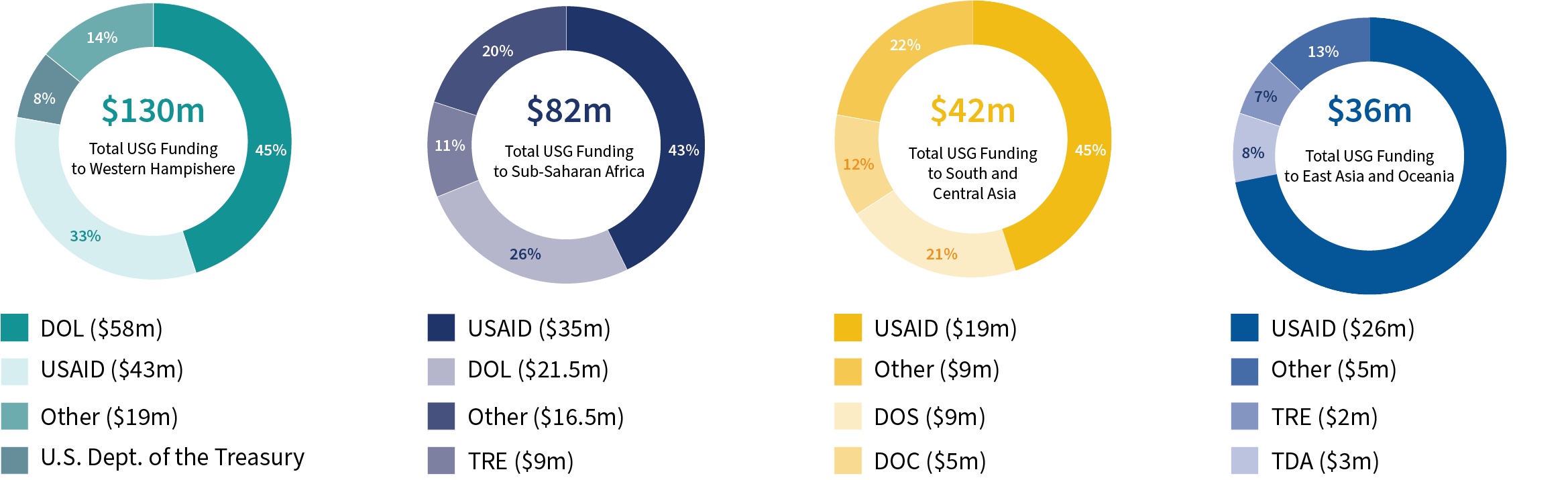
Regional Investment by Agency
Bilateral and Multilateral Assistance
Bilateral TCB assistance ($315m) between the United States and recipient states accounted for 84% of all TCB assistance, while 16% of TCB funding ($57m) was allocated to global, regional, and sub-regional programs.

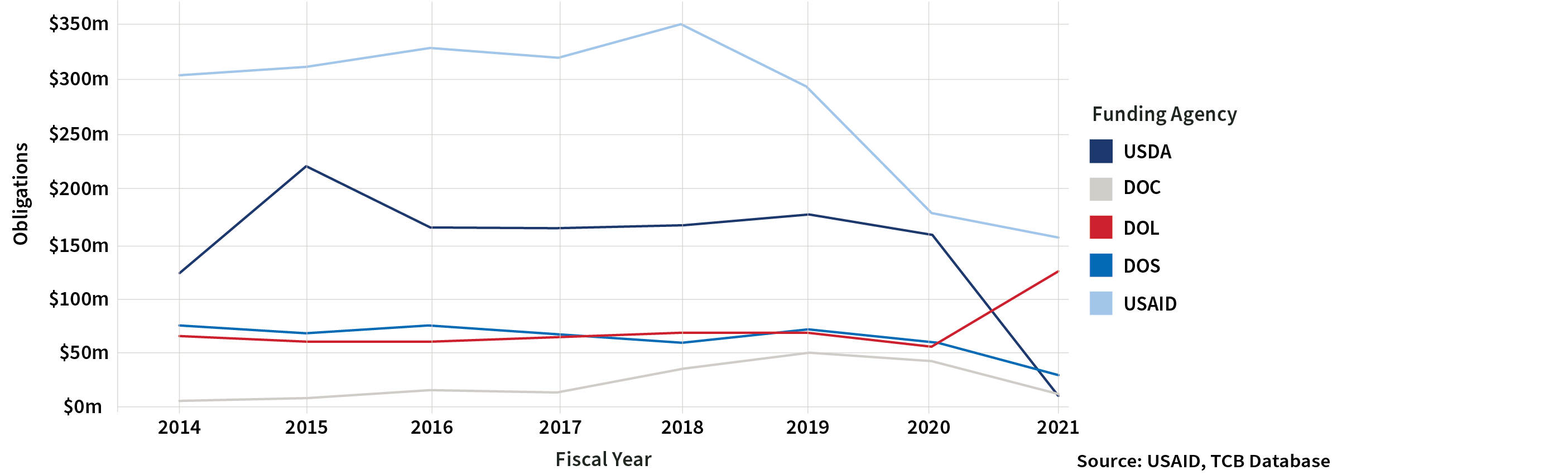
With the exception of Trade-related Labor, funding in all TCB funding categories declined for FY2021, possibly as a result of disruptions in programming arising from the COVID-19 pandemic. Note that the trends in U.S. Trade Capacity Building by Category do not include MCC obligations given that MCC reports all obligations under a single compact during the compact's first year, thus skewing category trends. While agriculture has historically been the TCB category with the highest funding, Trade-related Labor surpassed Agriculture as the largest category of TCB activities. The precipitous drop in TCB funding to Agriculture is due to decreased activities under the Department of Agriculture's Foreign Agricultural Services in FY 2021.